Why assess the SL level?
Why assess the social licence level?
Getting an overall assessment of your level of social licence is not that useful. What can you do with it? Brag? Worry? Put it in a report?
Risk management strategy
Far more useful is knowing which stakeholders give your organization a high versus low social licence and why. With that, you can develop a strategy to reduce your socio-political risk and open up socio-political opportunities.
Even more useful is knowing how the stakeholders are connected to each other. Are all the withhold social licences from groups that are tightly interconnected to one another and have links to powerful national or international actors? Are your supporters unconnected to each other and relatively isolated? If so, you have just discovered that you are facing a crisis situation.
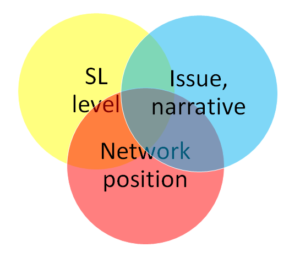 Useful social licence information comes from three types of data:
Useful social licence information comes from three types of data:
Measures of the social licence granted by each stakeholder.
The issues or narratives that each stakeholder mentions when talking about your organization or its activities.
The position of each stakeholder in the network of stakeholders (e.g., central, peripheral, bridging, coalition member, isolated, etc.).
Strategies for raising the social licence
The three types of data suggest strategies directly. In general, initiative that work involve some combination of collaborative decision-making with stakeholders and agreement on a larger -scale, or longer term goal or vision. For example, both criteria can be met with a multi-stakeholder, multi-sectoral round-table that defines priorities for a working relationship and shared future. The process of making decisions together, and following through, builds trust, which strengthens the relationships. The process of envisioning a shared future develops a positive narrative, which inoculates stakeholders against narratives that vilify your organization or activity. At the same time, a round-table changes the structure of the stakeholder network, often allowing supporters to strengthen bonds with each other and with ambivalent stakeholders. Even in situations that have become polarized, vociferous opponents can become supporters when they see that their perspectives are being respected and accommodated. A round-table also has the advantage of community transparency. Since everyone is present, self-serving opportunists have less chance of seeking personally advantageous side deals or special privileges.